|
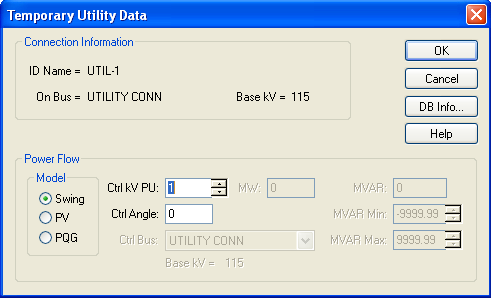
Model
|
The utility bus type used in modeling the power flow simulation. When you choose a model, those fields which are unavailable are dimmed.
- Swing: A swing bus holds the bus voltage and angle constant. To do this there cannot be limits on the amount of MW or MVAR the swing machine can accept or provide.
- PV: Constant power, constant voltage utility. This is also known as a regulated utility. This model tries to hold a user-specified bus voltage within utility MVAR limits.
- PQG: Constant power, constant var utility. This is also known as an unregulated utility. This model holds the MVAR generation within given voltage limits.
|
|
MW
|
The utility output MW. This may be actual operating or a rated value. This applies only to a PV or PQG utility.
|
|
MVAR
|
The utility output MVAR. This is only used when the utility is a constant power, constant var (PQG) machine or when a PV utility MVAR limit has been reached and the machine automatically switches to PQG.
|
|
MVAR Limits
|
The minimum and maximum MVAR limits for a regulated utility (PV). The utility will switch to type PQG if these limits are violated.
|
| Ctrl kV PU |
The desired control voltage for a regulated utility (PV). The utility will try to control the voltage at the controlled bus to a given value. If the utility bus is the swing bus, this voltage serves as the reference voltage. The voltage is entered in per-unit.
|
| Ctrl Angle |
Controlled angle is used only when a utility is designated as a swing utility. The value is entered in degrees.
|