IEC Equipment Duty Calculations
This topic describes the equipment duty calculations for breakers and fuses when your system is set to use the IEC standard.
HV Breakers
Initial Duty
- The bus X/R ratio and the maximum symmetrical current (device current) is considered for calculating the peak current.
- The device current can either be the branch current through the device or the difference of bus current and branch current.
- Duty amps is calculated by the formula:
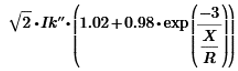
Breaking Duty
- If fault X/R is greater than test X/R, then the duty amps are:
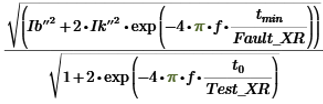
Where,
Ib – Breaking current at tmin
Ik” – Initial current
f – Frequency
to = Opening time of the breaker
tmin = Breaking time determined by the opening time of the breaker
|
t0(s) |
tmin(s) |
|---|---|
|
0 < t0 <0.05 |
0.02 |
|
0.05 <= t0 < 0.1 |
0.05 |
|
0.1 <= t0 <=0.1 |
0.1 |
|
0.25 <= t0 |
0.25 |
- If fault X/R is less than test X/R, then the duty amps are:
Device current at tmin
LV Breakers
- The fault X/R is compared with a standard test X/R taken from the table as per the standard 60947-2.
- If the fault X/R is smaller, the device current (symmetrical) becomes the duty amps.
- If the fault X/R is larger, then the device current (peak) is divided by a factor.
- The standard X/R table based on the breaking capacity of the breaker and the division factor for each category is given in the table below.
|
Breaking Capacity, Isym (kA) |
Test X/R |
Division Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 4.5 <= Isym <= 6 | 0.943 | 1.5 |
| 6 < Isym <= 10 | 1.782 | 1.7 |
| 10 < Isym <= 20 | 3.294 | 2.0 |
| 20 < Isym <= 50 | 4.023 | 2.1 |
| Isym > 50 | 4.966 | 2.2 |
HV and LV Fuses
- If fault X/R is greater than test X/R, then duty amps are:
- If fault X/R is less than test X/R, then duty amps are:
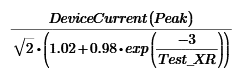
Device current (symmetrical)
