|
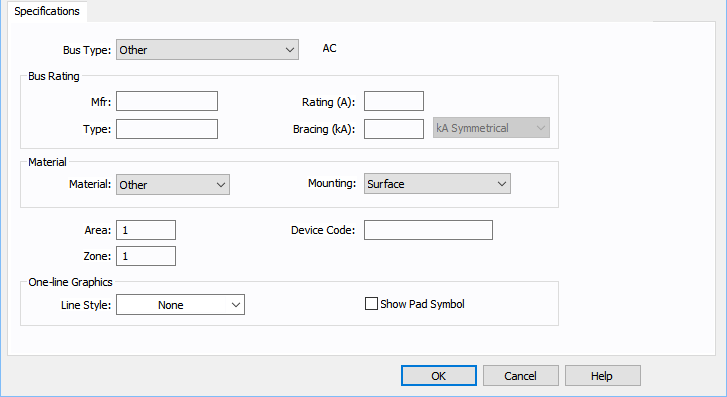
Bus Type
|
Type of equipment inside which the bus exists. The bus type definition is important for auto-design and arc flash hazard calculations. In arc flash hazard calculations, the parameters affected by type are the gap between conductors and the distance exponent. The various types are:
- Switchgear: This can be low voltage or high voltage switchgear.
- Open Air: The bus has no enclosures.
- Conductor: Wire ways, bus ways, and so on.
- MCC: Motor Control Center.
- Panel: Small and lighting panels.
- Panelboard: Low voltage power panelboards.
- Switchboard: This can be a low voltage or high voltage switchboard.
- NEMA E2 Contactor: NEMA E2 motor starter enclosures. The power voltage is at medium voltage. For low voltage control circuits this type can be used.
- Int Switch: Interrupting or disconnect or safety switch.
- VFD: Variable frequency drive or some type of motor drive.
- UPS: Uninterruptible power supply.
- ATS: Auto or manual transfer switch.
- Transformer Terminal: Enclosure transformer terminals/bushings.
- Vault: Underground space such as manhole for cable connections, transformers, and so on.
- Padmount Equipment: Padmount switches, padmount transformers cabinets, and so on.
- Control Panel: Enclosure for control circuits.
- Junction Box – Large: Large or deep junction box.
- Junction Box – Small: Small or shallow junction box.
- Network Protector: Spot or grid network protectors used in network distribution systems.
- Other: Any other type not specified.
|
|
Mfr
|
The manufacturer of the bus. User-defined, up to 15 characters.
|
|
Type
|
The type of bus rating. User-defined, up to 15 characters.
|
|
Rating (A)
|
Continuous current rating of the bus in amperes.
|
|
Bracing (kA)
|
Short circuit rating of bus bracing in kA. The testing standard unit is specified on the right as follows:
- A high voltage bus can have asymmetrical kA or peak kA (crest) units.
- A low voltage bus has symmetrical kA units.
|
|
Material
|
The material with which the bus is made. The options include copper, aluminum, or other.
|
|
Mounting
|
The method by which the bus is mounted. Options include flush, surface, or free standing.
|
|
Area
|
Area numbers are used to uniquely define different areas of the electrical system. These areas can then be used for creating specific text reports from analysis operations that represent subsets of the system. For example, typical paper plant areas may be the power house (Area 1), caustic plant (Area 2), pulp mill (Area 3), and paper machine (Area 4). Area numbers are positive integers between 1 and 999.
|
|
Zone
|
A zone number is simply a sub-area. This enables even more specific reporting. You may want to define the pulp mill as Area 3 and the digester electrical equipment as Zone 2. Specific reports can then be generated for this combination without including the entire pulp mill or the other digesters.
|
|
One-line Graphics – Line Style
|
The box drawn around the bus symbol in the one-line. Any line style can be selected from the box to represent an enclosure such as switchgear.
|
|
Device Code
|
You can type letters or numbers to describe the device code for the equipment item. The information can be converted and printed as a QR code on arc flash labels.
|
|
Show Pad Symbol
|
When this option is selected, a rectangular pad symbol is displayed below the bus on the one-line.
|