Control Tab
To set Power Flow options, from the Power Flow menu, select PF Options. You can also access the options from within the Database Edit focus by selecting Tools > Options > Analysis Options > Power Flow.
Select the Control tab to specify the behavior of a power flow study.
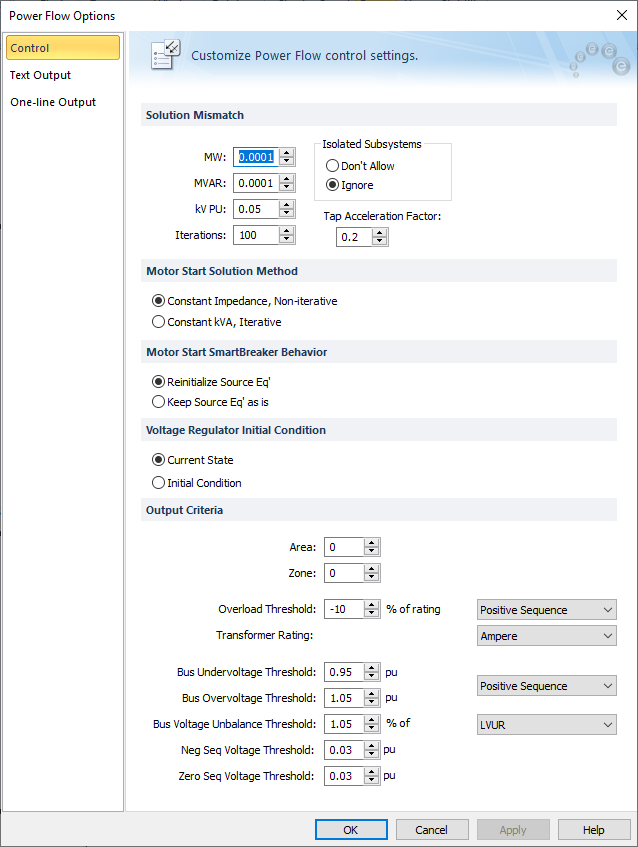
Figure 1: Control Tab of Power Flow Options Dialog Box
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Solution mismatch controls the tolerance of power flow convergence and how long convergence will take. The smaller the mismatch, the more difficult it becomes to make power flows and voltages converge to a solution. |
|
|
MW |
Convergence tolerance of the bus megawatts. Flows into a bus converging to within this tolerance of the actual load on the bus is considered to be an acceptable solution. The default setting of 0.0001 MW (100 watts) is an extremely accurate tolerance. |
|
MVAR |
Convergence tolerance of the bus megavars. Flows into a bus converging to within this tolerance of the actual load on the bus is considered to be an acceptable solution. The default setting of 0.0001 MVAR (100 vars) is an extremely accurate tolerance. |
|
kV PU |
This field determines the bus voltage tolerance for generator PQG buses that switch back to PV buses. Bus voltage must converge to within this tolerance of the actual load on the bus to be an acceptable solution. |
| Iterations |
Number of solution iterations allowed for convergence. For most typical industrial systems, only 20 iterations are required for convergence. If many load tap changers or tighter controls are used, 60 iterations may be required. |
| Isolated Subsystems |
All power flow solutions require a swing (slack) source to account for system losses, etc. (see Swing Sources). To solve an isolated system requires you or the program to add a swing source. An isolated subsystem is when a portion of the one-line is separated from the main part and does not have its own swing source (see below). This typically occurs when you open a feeder breaker on a radial line or transformer. It may also occur when opening multiple breakers on more complicated looped systems.
|
|
Tap Acceleration Factor |
Factor used to slow speed through iterations by changing LTC of transformer when changing taps. |
|
The motor start solution method controls the algorithm used and the way loads are modeled when motors are started in the power flow analysis. |
|
|
Constant Impedance, Non-iterative |
A direct solution method using the admittance matrix and voltages from the existing power flow solution. All constant kVA and current loads are converted to constant impedance loads for this method. Starting motors are also modeled as a constant impedance. The advantages of this method are its speed since the solution is direct (no iterations are required), and the fact that it cannot diverge. The disadvantage is that it may be non-conservative depending on the solution voltages. The reason for this is that constant impedance loads are a function of the square of the voltage. As the system voltage is reduced, the load is proportionally reduced also, effectively reducing the load. |
|
Constant kVA, Iterative |
An iterative method using the same algorithm as the power flow solution. All constant kVA, current, and impedance loads remain modeled as they are in a standard power flow solution. Starting motors are modeled as a constant impedance. The advantage of this method is its accuracy since it correctly models all load types. The disadvantage is that it can diverge (fail to solve) if the voltages become too low, or the loads are too high. |
|
Motor Start SmartBreaker Behavior The SmartBreaker feature enables you to open or close breakers, switches, and fuses while in the Power Flow focus and power flow or solve motor is performed automatically after breaker status changes. Starting from EasyPower 11.0, you can choose to either leave the source terminal voltage Eq’ as-is or resolve power flow to update the Eq’ during motor start when the breaker status changes. Note that this option only works in the Solve Motor mode. |
|
|
Reinitialize Source Eq’ |
After a breaker status change, solve power flow is run automatically to recalculate all the source internal voltage Eq’ and then the new Eq’ is used in the subsequent automatic Solve Motor action. This is consistent with how EasyPower worked in versions prior to 11.0. |
|
Keep Source Eq’ as is |
After a breaker status change, EasyPower uses the Eq’ before the breaker status change for the Solve Motor run. |
|
Voltage Regulator Initial Condition |
|
|
Current State |
Use this option to set the voltage regulator (transformer LTC tap) start from its current tap position at the beginning of the power flow solution. |
|
Initial Condition |
Use this option to set the voltage regulator (transformer LTC tap) start from initial condition (nominal tap) at the beginning of the power flow solution. |
| Output Criteria | |
|
Area |
Enables you to specify a specific bus area that will be reported in text results. |
| Zone |
Enables you to specify a specific bus zone that will be reported in text results. |
| Overload Threshold |
Sets the limit for flagging overload violations. Equipment items not in violation, yet within this threshold %, are highlighted for easy identification. This setting applies to both one-line output and text result output. For example, suppose a cable rated for 500A is loaded to 480A, and the Overload Threshold is set to -10 percent. The percent overload is determined as follows.
Note that the overload is negative, indicating that while the cable is not overloaded, it is 6 percent over the threshold limit of 10 percent. Therefore, it will be highlighted on the one-line when you click Overloads. You can also display the overload as a percentage of the equipment rating. To use this option, in the Database Edit focus, select Tools > Options, click System and select the Use 100% convention for displaying analysis overloads/overduties check box. In Unbalanced mode, you can choose the overload threshold based on either positive sequence or per phase. If you select positive sequence, then only the positive sequence loading and rating is used in overload calculation. If you choose the phase option, then the program compares the worst case, which is the heaviest loaded phase, to calculate overload. |
|
Transformer Rating |
Sets the transformer loading and rating based on Ampere or kVA.
|
|
Bus Undervoltage / Overvoltage Threshold |
Sets the minimum and maximum limit for determining voltage violations. Bus voltages that either exceed the maximum limit or drop below the lower limit are in violation. Buses in violation are highlighted on the one-line and printed in voltage violation text reports. In Unbalanced mode, you can select the option of Positive sequence, Line-to-Line, and Phase, which is the line-to-ground voltage used to calculate under or overvoltage. |
|
Bus Voltage Unbalance Threshold |
Sets the bus voltage unbalance threshold in percent. In Unbalanced mode, you can specify the unbalance threshold according to three options:
Buses voltage unbalances that exceed the maximum limit are in violation. Buses in violation are highlighted on the one-line and printed in voltage violation text reports. |
|
Neg. Seq. Voltage Threshold |
This option is only applicable to Unbalanced mode. It sets the negative sequence voltage maximum threshold. Bus negative sequence voltages that exceed the maximum limit are in violation. Buses in violation are highlighted on the one-line and printed in voltage violation text reports. |
|
Zero Seq. Voltage Threshold |
This option is only applicable to Unbalanced mode. This sets the zero sequence voltage maximum threshold. Bus zero sequence voltages that exceed the maximum limit are in violation. Buses in violation are highlighted on the one-line and printed in voltage violation text reports. |
