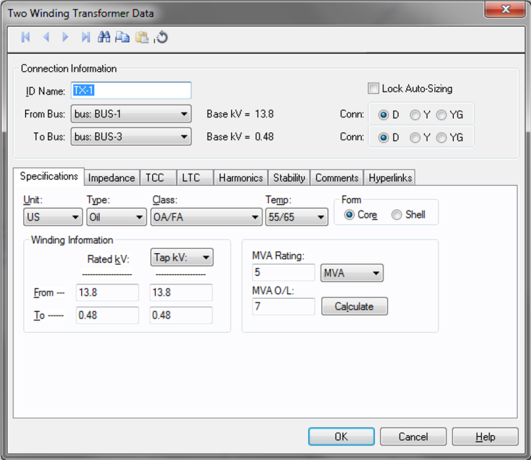
This dialog box includes the following areas and tabs:

Figure 1: Two-Winding Transformer Data Dialog Box
ID Name: Uniquely identifies the transformer. This ID name is sometimes referred to as the transformer name, and can be up to 12 characters long. The names default to TX-1, TX-2, TX-3, and so on as you enter new transformers on the one-line diagram, but you can change those names later if needed.
From Bus: The bus from which the transformer connects, which must already exist on the one-line. Ensure that the From Bus has approximately the same base kV as the transformer's From Rated kV. For reference, the From Bus base kV is displayed next to the bus name.
To Bus: The bus to which the transformer connects, which must already exist on the one-line. Ensure that the To Bus has approximately the same base kV as the transformer's To Rated kV. For your reference, the From Bus base kV is displayed next to the bus name.
Conn: The transformer winding connection type, which is either "Delta" (D), "Wye Ungrounded" (Y), or "Wye Grounded" (YG). If "Wye Grounded" is selected, grounding impedances can be entered on the Impedance tab in the Grounding area.
Lock Auto-Sizing: When this is checked, Auto-Design does not change the size of the transformer.
Unit: Choose either U.S. or Metric.
Type: Type of transformer (oil, gas, dry, silicone, or vapor). This field is used to determine the rating capacity of the transformer for the power flow overload solution.
Class: Type of cooling used by the transformer. Various combinations of forced air, water and forced oil are available. This field is used to determine the rating capacity of the transformer for the power flow overload solution.
Temp: ANSI temperature rating of the transformer. Various combinations can be chosen and are dependent on the type of transformer. Dual ratings such as 55/65 increase the overload capability of the transformer by 12 percent.
Form: Either core or shell type transformers can be selected. This value is for reference only and does not affect analysis.
Rated kV: Rated kV of a winding. The rated kV can be different than the base kV or the tap kV. EasyPower automatically adjusts the model to account for different taps, turns ratio and bases you choose.
Tap kV / Tap%: Tap kV of a winding. You can also specify the tap kV in terms of percentage of the rated value. If the actual tap kV is not known, enter the rated kV. Load tap changer control can be used to determine final tap settings if needed. EasyPower automatically adjusts the model to account for different taps, turns ratio and bases you select.
Rated: Self cooled rating of the transformer. Use to select the unit in MVA or kVA.
MVA O/L: The overload rating as filled in using the Calculate button or you can type in a different rating.
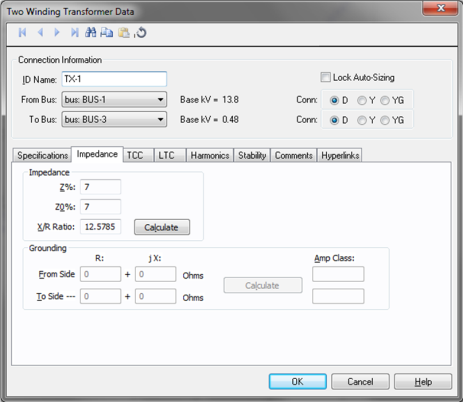
Figure 2: Impedance tab of Two-Winding Transformer Dialog Box
Z: Transformer nameplate impedance in percent. By definition, this is the positive sequence leakage impedance in percent on the self-cooled MVA and nominal voltage rating. The strict definition is the percent of rated voltage impressed on the high voltage winding to produce rated full load current in the short circuited low voltage winding.
Z0: Transformer zero sequence leakage impedance in percent. If you don't know this value, enter the positive sequence impedance (Z) for shell transformers (see Form field above). For core transformers, use approximately 85% of Z. If you enter this value as zero (0.0), the positive sequence impedance is used.
X/R Ratio: Transformer reactance to resistance ratio, which is used to determine resistance value.
Calculate: Fills in a computed value for the X/R field, based on the transformer's MVA rating. You can override this value by typing in a different number. The calculated X/R ratio curve is based on the medium ANSI Standard curve [ANSI C37.010-1979]. This curve was developed mainly for power transformers and is typically high for low voltage unit substations less than 2500 kVA.
Grounding impedances only apply to wye grounded connections. The units are R+jX in ohms. If you only know the ground amperes of the circuit, enter the amp class and use the Calculate button to calculate the grounding impedance.
R: Transformer neutral ground resistance in ohms. This is the most common method of grounding the transformer neutral winding. Grounding resistors are usually given in amperes. The impedance is found from the following equation.
R = Vln / I
If the transformer is grounded through a separate grounding transformer with a secondary resistance, this resistance must be converted to the primary winding. Only wye grounded transformers are modeled with grounds. Mid or corner tapped delta windings are not modeled.
jX: Transformer neutral ground reactance in ohms.
Amp Class: This is the current in amps through the ground impedance at the rated voltage. You can enter data in this field directly in Amps or calculate it based on the voltage and ground impedance R +jX using Calculate.
TCC for information.
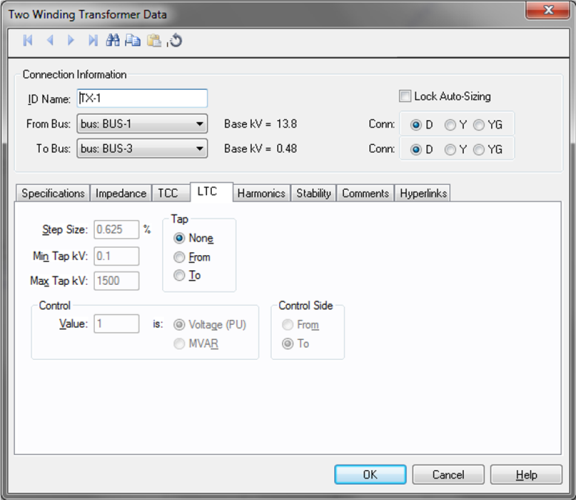
Figure 3: LTC tab of Two-Winding Transformer Data Dialog Box
Tap: Load tap changer (LTC) position can be placed on either side of the transformer by selecting From or To. If the transformer does not have an LTC, select None for standard fixed taps. Fixed off-nominal taps can be entered in the main dialog's Tap kV field.
Step Size: The default is 0.625 but you can type in your own percentage step size both here and in the power flow two-winding transformer temporary dialog box.
Min Tap kV: Minimum tap kV, which is used to determine the bottom limit that the tap can be adjusted to during a power flow analysis. This value should be the lowest tap on the transformer to get meaningful results. The default of 0.12 kV is not realistic and should be changed to the actual values if the LTC is used.
Max Tap kV: Maximum tap kV, which is used to determine the upper limit that the tap can be adjusted to during a power flow analysis. This value should be the highest tap on the transformer to get meaningful results. The default of 1500 kV is not realistic and should be changed to the actual values if the LTC is used.
Control Value: Control value, which is determined by the Control Type field.
Control Type: Determines how the LTC model is used.
Control Side: The LTC can control the voltage or MVAR on either side of the transformer, regardless of which side the tap is located.
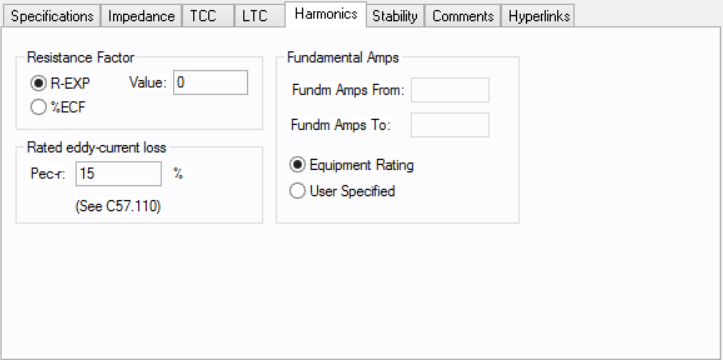
Use the Harmonics tab to indicate whether this equipment item is introducing harmonics into your power system.
EasyPower offers two methods for calculating RH:
RH = RFund * H R-EXP
RH = RFund * (1+ECF*H2)/(1+ECF)
EasyPower defaults all skin effect correction to R-EXP and a value of 0.5.
| R-EXP | %ECF | |
|---|---|---|
|
Transformer |
0.5-1.0 |
1.0-3.0 |
|
Utility |
0.0-0.8 |
- |
|
Generator |
0.3-0.6 |
- |
|
Line/Cable |
0.5 |
- |
|
Reactor |
0.5-1.0 |
0.8-3.0 |
|
Motor |
0.2-0.4 |
- |
Use to set the fundamental amps. The options are as follows:
To use fundamental current calculated by power flow, select Calculated from Power Flow in the Summation Fundamental Voltage area of the Harmonics Options > Control dialog box.
For a two-winding transformer, the options are:
Fundm Amps From: Calculated rated amps on the primary (from) side.
Fundm Amps To: Calculated rated amps on the secondary (to) side.
Rated eddy-current loss, Pec-r: Eddy-current loss under rated conditions expressed as a percentage of rated I2R loss.
Figure 4: Stability Tab
Mfr: Provides a list of transformer manufacturers available in the device library. If the desired manufacturer is not listed in the device library, you can add it to the library.
Type: Transformer types available from the manufacturer chosen in the Mfr field above. If the type you want is not listed, you can add it to the library.
Model: Lists available transformer models in the library.
 Lib: Populates transformer data from the library.
Lib: Populates transformer data from the library.
This tab is read-only and appears only if you have imported data from an SKM Data Format file. See Importing an SKM Format File for more information.
See Comments for information.
See Hyperlinks for information.
| Database Technical Reference |