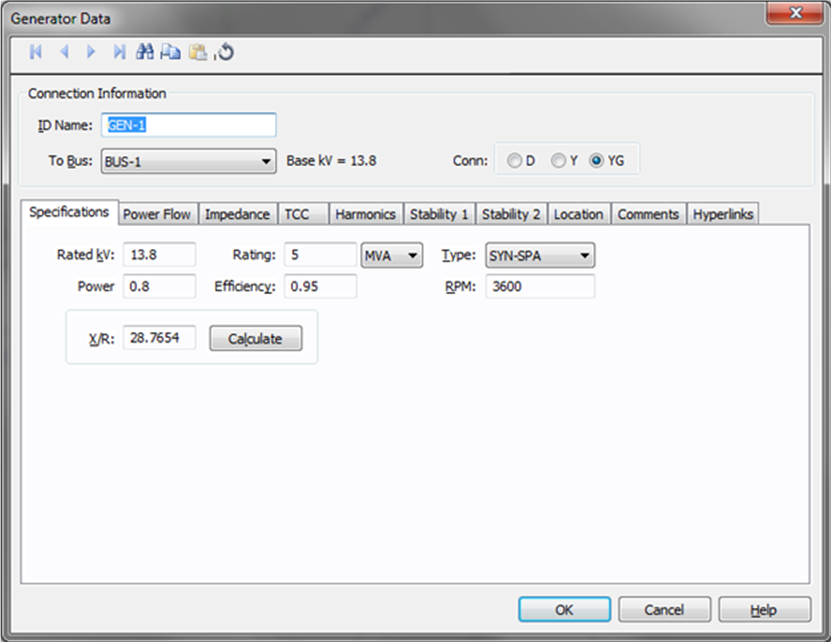
Figure 1: Generator Data Dialog Box
This dialog box includes the following areas and tabs:

Figure 1: Generator Data Dialog Box
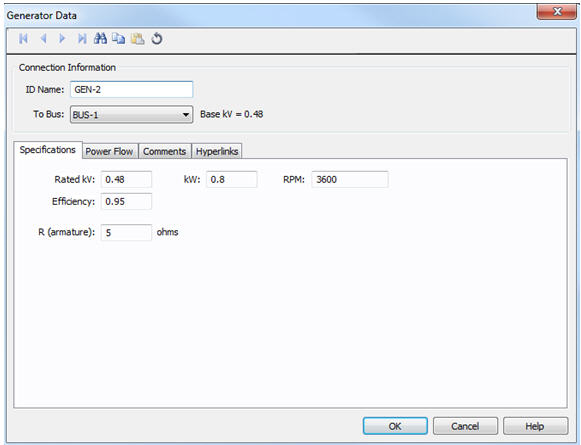
Figure 3: DC Generator Specifications Tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Rated kV | Name plate rated voltage in kV. |
| kW | Name plate (rated) power in kW. |
| RPM | Rated speed in revolutions per minute. |
| Efficiency | Efficiency in per unit. |
| R (armature) | Internal resistance of the DC generator in ohms. |
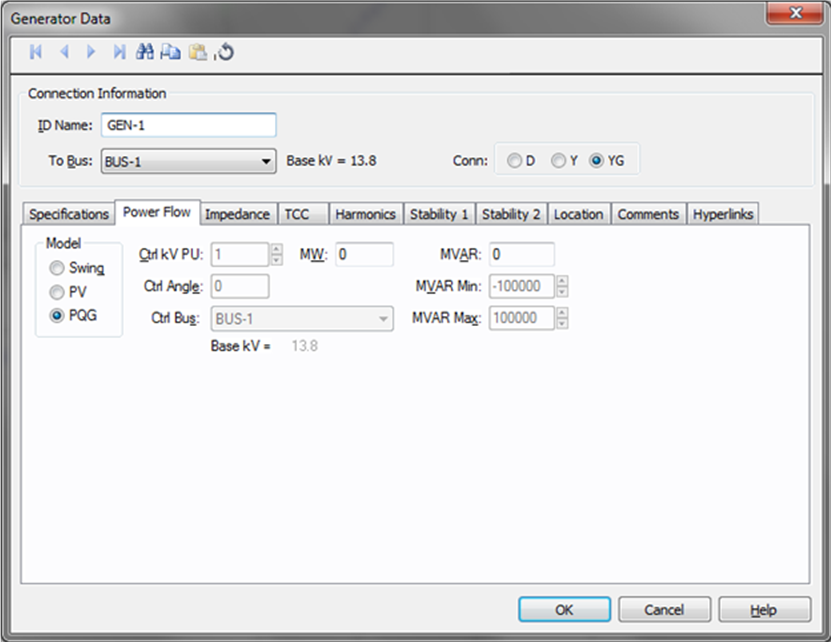
Figure 4: Power Flow tab of Generator Data Dialog Box
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Model |
Generator bus type used in modeling the power flow simulation. When you select a particular model, those fields that do not apply become unavailable.
|
| Ctl kV PU | Desired control voltage for a regulated generator (PV). The generator will try to control the voltage at the controlled bus to a given value. If the generator bus is the swing bus, this voltage serves as the reference voltage. The voltage is entered in per-unit. |
| Ctl Angle | Controlled angle is used only when a generator is designated as a swing bus. The value is entered in degrees. |
| Ctrl Bus |
For a PV generator (regulated), the bus that is to be controlled to the control voltage. If this field is blank in the database, EasyPower fills it in with the name of the bus listed in the To Bus field. (Note that this does not take effect until you accept it by clicking OK to close the database dialog box.) This field is ignored if the Model is set to Swing. |
| MW | Generator output MW. This may be actual operating or a rated value. This applies only to a PV or PQG generator. |
| MVAR | Generator output MVAR. This is only used when the generator is a constant power, constant var (PQG) machine or when a PV generator MVAR limit has been reached and the machine automatically switches to PQG. |
| MVAR Limits | Minimum and maximum MVAR limits for regulated generators (PV). The generator will switch to type PQG if these limits are violated. If there is only one swing generator (Model = “Swing”) on a bus, it should not have any MVAR limits. If there are more than one swing generators on a bus, at least one of them must be unlimited. |
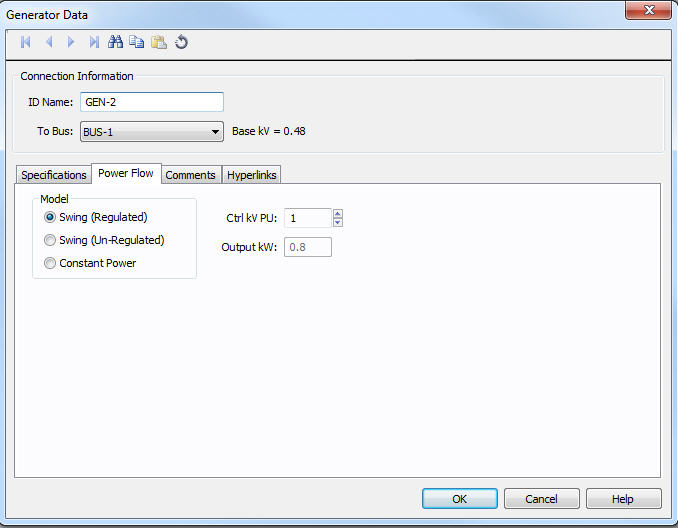
Figure 5: DC Generator Power Flow tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Model |
DC generators have three control modes:
|
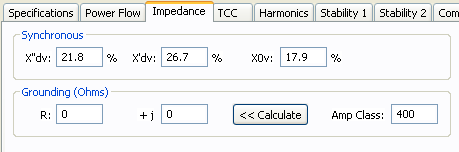
Figure 6: Impedance Tab of Generator Data Dialog Box
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| X”dv | Subtransient reactance in percent on generators MVA base. Most synchronous generators have subtransient reactances in the 9-20% range1Short Circuit Calculations, General Electric , GET 3550. . The subtransient reactance is used for ½ cycle, 5 cycle and 30 cycle short circuit calculations in accordance with ANSI Standards. |
| X’dv | Transient reactance in percent on generators MVA base. This value typically ranges from 15-30%. The transient reactance is not used in ANSI standard calculations except for hydro and salient pole generators without amortisseur windings (Xpu = 0.75X’). |
| X0v | Zero sequence reactance in percent on generators MVA base. This value may range from 3-15% for typical generators. Zero sequence values are used in all ground fault calculations. |
| Xlr | Locked rotor impedance for induction machines. When actual data is not available, use 16.7%. |
| Ground R |
Generator neutral ground resistance in ohms. This is the most common method of grounding generator neutrals and is usually given in amperes. The impedance is found from the following equation. R = Vln / I If the generator is grounded through a grounding transformer with a secondary resistance, this resistance must be converted to the primary winding. If you know the Amp value for the resistor, you can enter the amp value in the Amp Class field and use the Calculate button to find the resistance. |
| Ground jX | Generator neutral ground reactance in ohms. |
| Amp Class | This is the current in amps through the ground impedance at the rated voltage. You can enter data in this field directly in Amps or calculate it based on the voltage and ground impedance R +jX using the Calculate button. |
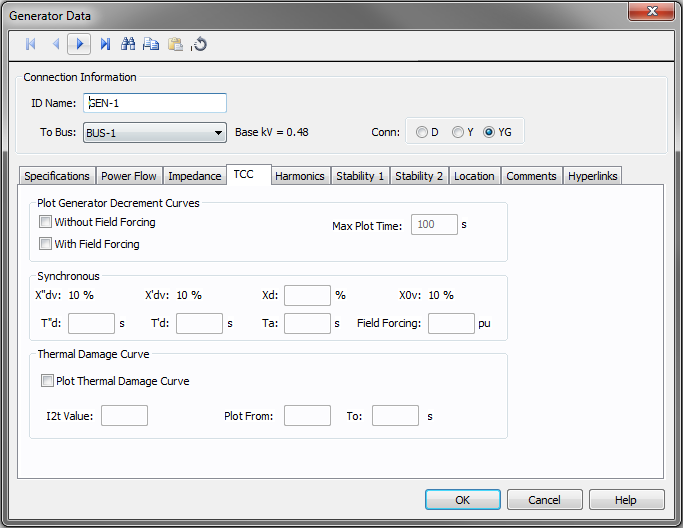
Figure 7: TCC tab of Generator Data dialog
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Plot Generator Decrement Curves |
You can plot short circuit decrement curves “with” and “without” excitation field forcing for comparison purposes.
|
| Synchronous | |
| Xd | Synchronous reactance of the generator, expressed as a percent. |
| T”d | Direct axis sub-transient short circuit time constant. |
| T’d | Direct axis transient short circuit time constant in seconds. |
| Ta |
Armature time constant in seconds. A typical generator datasheet will provide the Ta value. However, some manufacturers may not provide Ta in the datasheet. The armature time constant is associated with the rate of change of dc current in the stator when the generator is subjected to a 3-phase fault. Ta for different types of generators is provided in the book “Power System Control and Stability,” by Paul M. Anderson and A. A. Fouad, IEEE Press, 1994. Ta = (Ld’ + Lq) / 2r Where Ld’ is the d axis transient inductance and Lq is q axis inductance. A typical value of Ta is 0.15 seconds for fault on the machine terminal. Prabha Kundur’s book “Power System Stability and Control”, McGraw-Hill, 1994, provides the following equation for Ta: Ta = (Ld” + Lq”) / 2/ Ra Typical value for Ta lies between 0.03 and 0.35s. |
| Forcing Field |
Forced excitation current at a given load expressed as per unit value of field current at no load, Ifd0. |
| Thermal Damage Curve
This section allows you to plot “I^2t” thermal damage curve for the generator. |
|
| Plot Thermal Damage Curve | Select this check box to enable plotting of the damage curve and to enter data for this section. |
| I2t Value | This defines the (I^2)t line for the damage curve. I is in per-unit of generator rated current and t is in seconds. If I2t Value is 20, then the extrapolated damage curve line would intersect with the FLA of the generator at 20 seconds. |
| Plot From/To | The damage curve is drawn on the TCC plot within these values as the lower and upper limits in seconds. |
Use the Harmonics tab to indicate whether this equipment item is introducing harmonics into your power system.
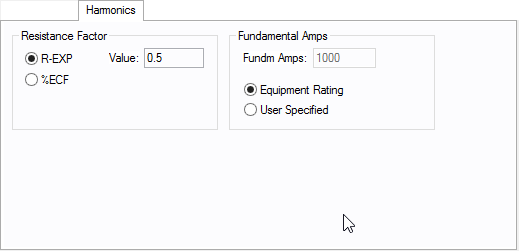
Figure 8: Harmonics Tab
| Option | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance Factor |
EasyPower offers two methods for calculating RH:
RH = RFund * H R-EXP RH = RFund * (1+ECF*H2)/(1+ECF) EasyPower defaults all skin effect correction to R-EXP and a value of 0.5.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Fundamental Amps |
Use to set the fundamental amps. The options are as follows:
To use fundamental current calculated by power flow, select Calculated from Power Flow in the Summation Fundamental Voltage area of the Harmonics Options > Control dialog box. |
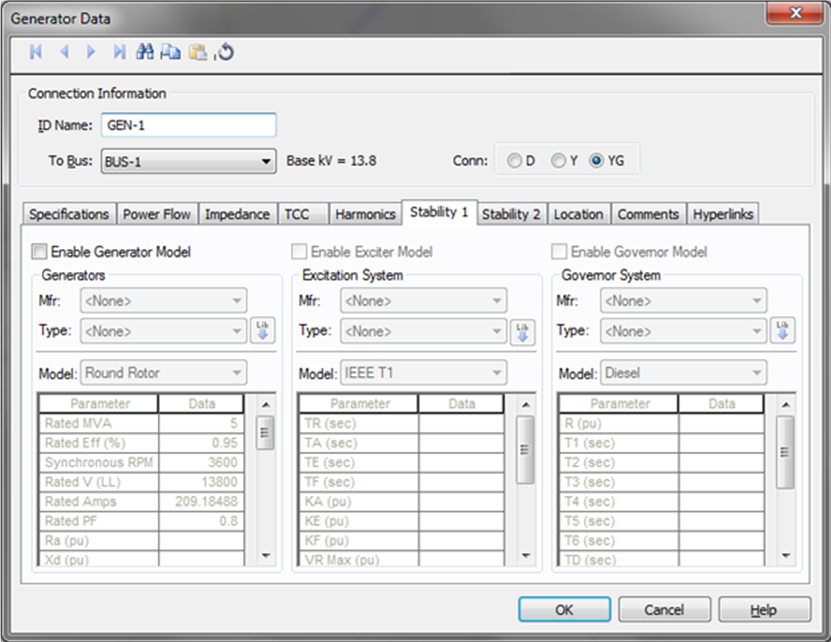
Figure 9: Stability 1 Tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Generator Model | Enables stability data entry for the generator model. |
| Mfr | Provides a list of generator manufacturers available in the device library. If the desired manufacturer is not listed in the device library, you can add it to the library. |
| Type | Generator types available from the manufacturer chosen in the Mfr field above. If the desired type is not listed, you can add it to the library. |
| Model | Lists available generator models in the library. |
 Lib Lib
|
Populates generator data from the library. |
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Exciter Model | Enables stability data entry for the exciter model. |
| Mfr | Provides a list of exciter manufacturers available in the device library. If the desired manufacturer is not listed in the device library, you can add it to the library. |
| Type | Exciter types available from the manufacturer chosen in the Mfr field above. If the desired type is not listed, you can add it to the library. |
| Model | Lists available exciter models in the library. |
 Lib Lib |
Populates exciter data from the library. |
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Governor Model | Enables stability data entry for the governor model. |
| Mfr | Provides a list of governor manufacturers available in the device library. If the desired manufacturer is not listed in the device library, you can add it to the library. |
| Type | Governor types available from the manufacturer chosen in the Mfr field above. If the desired type is not listed, you can add it to the library. |
| Model | Lists available governor models in the library. |
 Lib Lib |
Populates governor data from the library. |
For details on the parameters, see Dynamic Stability . For information about the library, see EasyPower Device Library.
Figure 10: Stability 2 Tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Stabilizer Model | Enables stability data entry for the stabilizer model. |
| Mfr | Provides a list of stabilizer manufacturers available in the device library. If the desired manufacturer is not listed in the device library, you can add it to the library. |
| Type | Stabilizer types available from the manufacturer chosen in the Mfr field above. If the desired type is not listed, you can add it to the library. |
| Model | Lists available stabilizer models in the library. |
 Lib Lib |
Populates stabilizer data from the library. |
For details on the parameters, see Dynamic Stability . For information about the library, see EasyPower Device Library.
See Location for more information.
This tab is read-only and appears only if you have imported data from an SKM Data Format file. See Importing an SKM Format File for more information.
See Comments for information.
See Hyperlinks for information.
| Database Technical Reference |

|