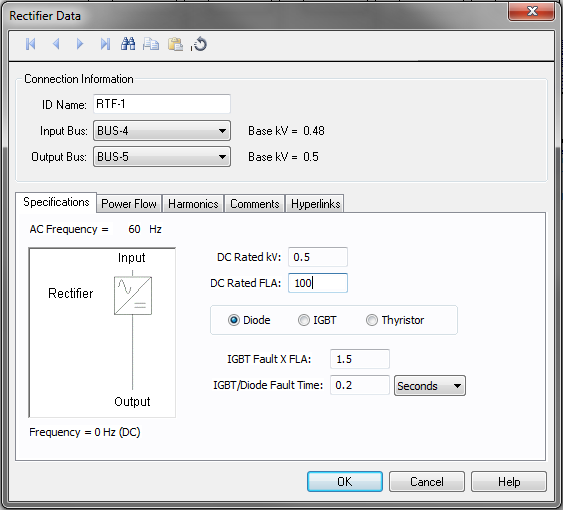
Figure 1: Rectifier Data Dialog Box
This dialog box includes the following areas and tabs:
See also:

Figure 1: Rectifier Data Dialog Box
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| DC Rated kV | Name plate voltage rating of DC output in kV. |
| DC Rated FLA | Name plate current rating of DC output in amps. |
| Type | Specify the component for the rectifier. Select from Diode, Thyristor and IGBT. This affects power flow simulation methods. Diode and Thyristor types use Kimbark’s equations to determine the real and reactive power on the Rectifier input, and to control DC voltage or current. The IGBT type controls power factor and voltage. Control fields are specified in the Power Flow tab. |
| Fault FLA | Expected fault current on the DC side, in multiples of full load amp rating. |
| Fault Time/Block Time | Duration the fault current will last. The unit can be seconds or cycles. |
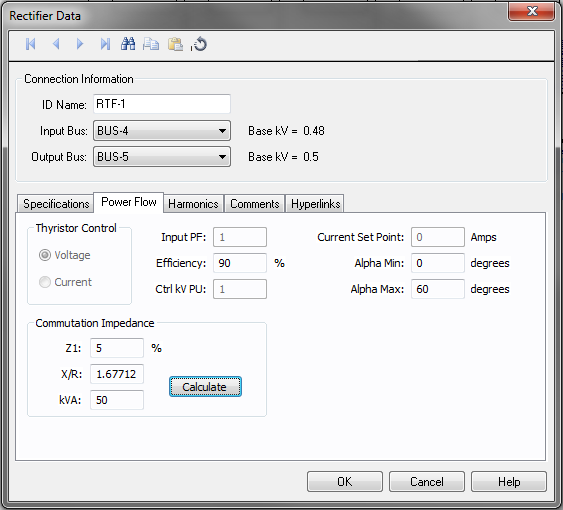
Figure 2: Rectifier Data – Power Flow tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Thyristor Control |
When the rectifier type is thyristor, the control can be one of the following:
|
| Commutation Impedance |
Commutation impedance is used to calculate the power flow using Kimbark’s equations. The rectifier must be fed by a dedicated transformer, where the characteristics are also defined here:
|
| Input PF | When the rectifier type is IGBT, this specifies the control input power factor. |
| Efficiency | Ratio of output power to input power in percent. |
| Ctrl kV PU | For IGBT type or voltage control thyristor type, this is the controlled output voltage in per unit. |
| Current Set Point | The fixed value of output current in Amps for current controlled thyristor type. |
| Alpha Min | Minimum firing angle of the rectifier. |
| Alpha Max | Maximum firing angle of the rectifier. |
Use the Harmonics tab to indicate whether this equipment item is introducing harmonics into your power system.
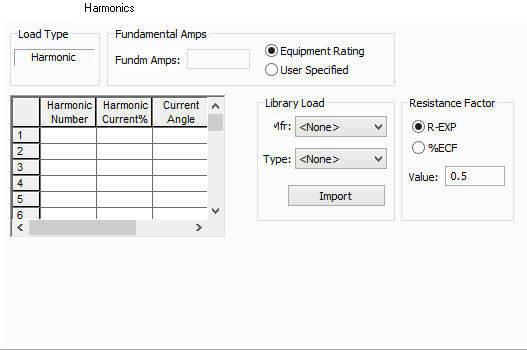
Figure 3: Harmonics Tab
| Option | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load Type |
The default is Linear, indicating the equipment does not produce harmonics. Choosing Harmonic makes the item an harmonic source and makes other fields in this tab available to edit. Note:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Fundamental Amps |
Use to set the fundamental amps. The options are as follows:
To use fundamental current calculated by power flow, select Calculated from Power Flow in the Summation Fundamental Voltage area of the Harmonics Options > Control dialog box. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Harmonic Spreadsheet |
Use the spreadsheet to enter the harmonic spectrum produced by this item. You can enter up to 30 different harmonics in each equipment item. In the spreadsheet, enter the Harmonic Number (such as 5 for the 5th harmonic), the Harmonic Current in percent of the Fundamental Amps, and the Current Angle. By indicating the current angle, you can simulate transformer phase shift effects on rectifiers so appropriate canceling can take place. The harmonic may be integer or non-integer. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Library Load |
Common harmonic spectra may be entered from the device library. For instructions on how to enter your own spectra information, see Harmonics with Spectrum™. After selecting a particular device library spectrum from the Mfr and Type lists, click Import, and that spectrum is entered into the harmonic spreadsheet. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Resistance Factor |
EasyPower offers two methods for calculating RH:
RH = RFund * H R-EXP RH = RFund * (1+ECF*H2)/(1+ECF) EasyPower defaults all skin effect correction to R-EXP and a value of 0.5.
|
This tab is read-only and appears only if you have imported data from an SKM Data Format file. See Importing an SKM Format File for more information.
See Comments for information.
See Hyperlinks for information.
| Database Technical Reference | |
| Notes on Rectifier Modeling | |
| Notes on Rectifier Power Flow Modeling |

|