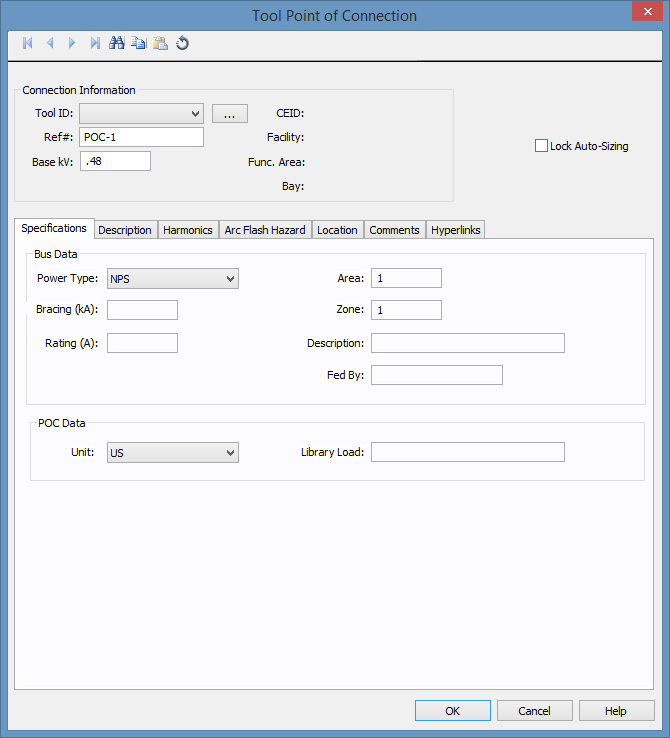
Figure 1: Tool Point of Connection Data Dialog Box
Use the tool point of connection to connect a tool to the one-line. A tool is a piece of equipment that can potentially have multiple different points of connection to the electrical system.
The point of connection represents the combination of both a bus and a load. This combination enables you to perform arc flash calculations on the bus and load as a unit.
This dialog box includes the following areas and tabs:

Figure 1: Tool Point of Connection Data Dialog Box
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Tool ID | The identifier for the tool. You can select from the list, or click Browse to create a new tool. See Edit Tools for more information. |
| Ref# |
The reference number for the point of connection. This information appears on the one-line. |
| Base kV | Base kV for the tool point of connection. Note that the tool point of connection must have a kV entered before equipment can be connected to it. Anything less than 1 kV is considered low voltage, anything 1 kV or more is high voltage. |
| CEID | Copy Exactly Identifier. This represents a type of tool. |
| Facility | The facility where the tool point of connection exists. This information comes from the tool. See Edit Tools for more information. Facilities are set up under Tools > Options > Facilities. |
| Func. Area | The functional area where the tool point of connection exists. This information comes from the tool. See Edit Tools for more information. |
| Bay | The bay where the tool point of connection exists. This information comes from the tool. See Edit Tools for more information. |
| Lock Auto-Sizing | When this check box is selected, the tool point of connection cannot be auto-sized. |
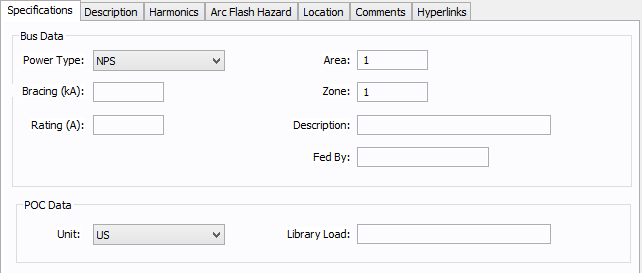
Figure 2: Specifications Tab
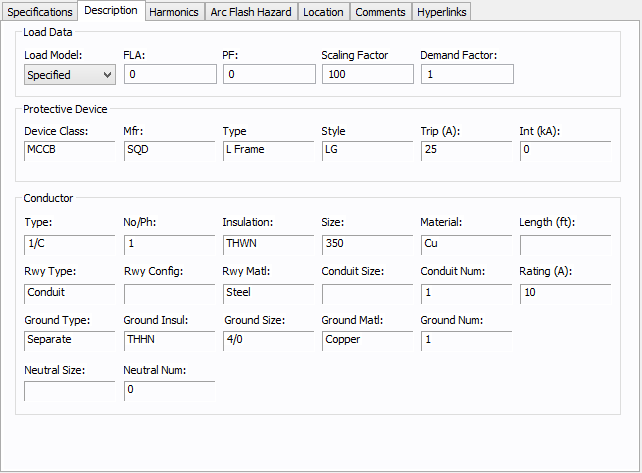
Figure 3: Description Tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Model | Select from Specified (user-entered) data or from SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) data. SCADA data can be read in by clicking the  EasyPower button and then clicking Import . EasyPower button and then clicking Import . |
| FLA | Full load amps (rated continuous current) of the load. The point of connection load is treated as a constant kVA load model when performing power flow calculations. |
| PF | Power factor for the load. |
| Scaling Factor | Each load can be varied by applying a different scaling factor. This lets you model the actual panel or lumped load on a bus, then study different loading conditions. This allows quick “what if” studies and prevents errors that occur from data entry. |
| Demand Factor | Demand factor for the load. |
| Protective Device |
The protective device information comes from the breaker located between the point of connection and the bus. |
| Conductor |
The conductor information comes from the cable that joins the point of connection with the bus. |
Use the Harmonics tab to indicate whether this equipment item is introducing harmonics into your power system.
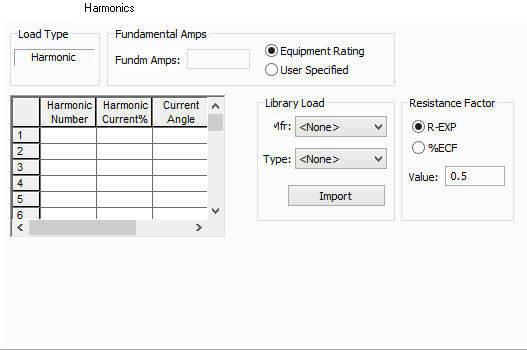
Figure 4: Harmonics Tab
| Option | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load Type |
The default is Linear, indicating the equipment does not produce harmonics. Choosing Harmonic makes the item an harmonic source and makes other fields in this tab available to edit. Note:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Fundamental Amps |
Use to set the fundamental amps. The options are as follows:
To use fundamental current calculated by power flow, select Calculated from Power Flow in the Summation Fundamental Voltage area of the Harmonics Options > Control dialog box. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Harmonic Spreadsheet |
Use the spreadsheet to enter the harmonic spectrum produced by this item. You can enter up to 30 different harmonics in each equipment item. In the spreadsheet, enter the Harmonic Number (such as 5 for the 5th harmonic), the Harmonic Current in percent of the Fundamental Amps, and the Current Angle. By indicating the current angle, you can simulate transformer phase shift effects on rectifiers so appropriate canceling can take place. The harmonic may be integer or non-integer. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Library Load |
Common harmonic spectra may be entered from the device library. For instructions on how to enter your own spectra information, see Harmonics with Spectrum™. After selecting a particular device library spectrum from the Mfr and Type lists, click Import, and that spectrum is entered into the harmonic spreadsheet. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Resistance Factor |
EasyPower offers two methods for calculating RH:
RH = RFund * H R-EXP RH = RFund * (1+ECF*H2)/(1+ECF) EasyPower defaults all skin effect correction to R-EXP and a value of 0.5.
|
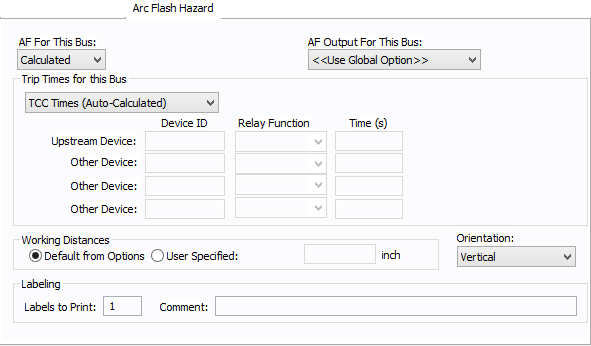
Figure 5: Arc Flash Hazard Tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| AF For This Bus |
Specify how you would like arc flash results determined for this bus. Calculated: When calculated is selected, Trip times for this bus and Working Distances sections become available. Excluded: Select to exclude the bus from arc-flash reports. Some examples of when excluded might be selected are buses that are on utility side (not worked on by company employees) but still modeled on the one-line and buses where energized work is not likely (splices). Forced To: When selected an additional cell will appear where you can enter the incident energy for this bus. The arc flash value incident energy entered for this bus is shown on the one-line and in the Arc Flash Hazard Report. This is typically used for buses where the NFPA-70E has stated a particular PPE level can be assumed if certain conditions exist. Particularly, 208 volt equipment fed by 125 KVA or smaller transformers. |
| AF Output For This Bus |
This specifies whether to display results on the line side or the load side of the Main protective device of the bus equipment. If the arc flash hazards output for this bus needs to be different from the global option, use this field. The choices are:
|
| Trip Times for this Bus |
Select method for determining trip times for this bus by choosing on the following:
|
| Working Distances |
Specifies the working distances shown on the one-line and in the arc flash hazard report.
|
| Orientation |
This is the orientation of the bus with respect to a worker that may be exposed to arc flash. This is not related to the vertical and horizontal buses in MCC and Switchgear. Arc travels away from the source and extends from the tip of the conductors. Based on the orientation of the conductors, the incident energy can vary. This choice affects the calculations factor (Cf) used in the arc flash hazard equations. See Orientation for more information. |
| Labels to Print | Enter the number of labels you want to print for arc flash hazard analysis. If you enter "0," no labels will print. |
| Comment | Use to add a comment to the arc flash label. |
See Location for more information.
This tab is read-only and appears only if you have imported data from an SKM Data Format file. See Importing an SKM Format File for more information.
See Comments for information.
See Hyperlinks for information.
| Database Technical Reference | |
| Edit Tools |

|