Generator - Power Flow Tab
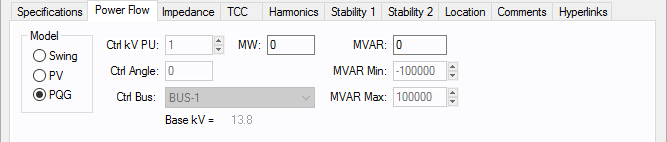
Figure 1: Power Flow tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Generator bus type used in modeling the power flow simulation. When you select a particular model, those fields that do not apply become unavailable.
|
|
|
Desired control voltage for a regulated generator (PV). The generator will try to control the voltage at the controlled bus to a given value. If the generator bus is the swing bus, this voltage serves as the reference voltage. The voltage is entered in per-unit. |
|
|
Controlled angle is used only when a generator is designated as a swing bus. The value is entered in degrees. |
|
|
Ctrl Bus |
For a PV generator (regulated), the bus that is to be controlled to the control voltage. If this field is blank in the database, EasyPower fills it in with the name of the bus listed in the To Bus field. (Note that this does not take effect until you accept it by clicking OK to close the database dialog box.) This field is ignored if the Model is set to Swing. Note: To set the control bus for a single-phase utility or generator, you must make the connection on the one-line. . |
|
MW |
Generator output MW. This may be actual operating or a rated value. This applies only to a PV or PQG generator. |
|
MVAR |
Generator output MVAR. This is only used when the generator is a constant power, constant var (PQG) machine or when a PV generator MVAR limit has been reached and the machine automatically switches to PQG. |
|
MVAR Limits |
Minimum and maximum MVAR limits for regulated generators (PV). The generator will switch to type PQG if these limits are violated. If there is only one swing generator (Model = “Swing”) on a bus, it should not have any MVAR limits. If there are more than one swing generators on a bus, at least one of them must be unlimited. |
DC Generator Power Flow Tab
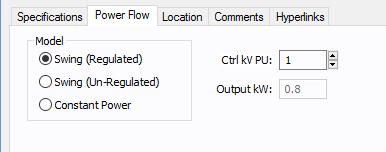
Figure 2: DC Generator Power Flow tab
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Model |
DC generators have three control modes:
|
|
Ctrl kV PU |
This is the scheduled per-unit voltage that the voltage control unit will try to maintain for the generator. This applies only to the Swing (Regulated) model. |
|
Output kW |
This is the scheduled output kW value that the generator will deliver to the system. This is applicable only to Constant Power. |
More Information
- Generator Data
- Database Dialog Box Toolbar
- Generator - Connection Information
- Generator - Specifications Tab
- Generator - Impedance Tab
- Generator - TCC Tab
- Generator - Harmonics Tab
- Generator - Stability 1 Tab
- Generator - Stability 2 Tab
- Generator - Reliability Tab
- Generator - Location Tab
- Generator - Comments Tab
- Generator - Hyperlinks Tab
- Generator - Collected Data Tab
- Generator - Media Gallery Tab
