Motor - Power Flow Tab
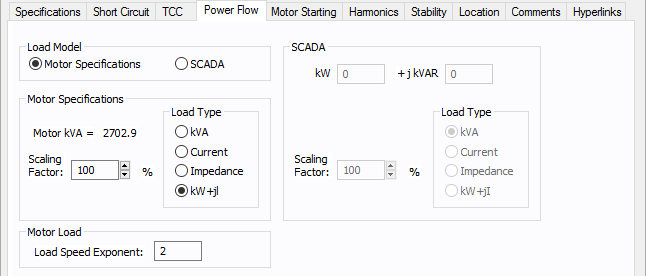
Figure 1: Power Flow Tab of the Motor Data Dialog Box
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Load Model |
Enables you to select the motor kVA from the Specified data or from SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) data. SCADA data can be read in by clicking File > Import. |
| Motor Specifications | |
|
Motor kVA |
Calculated from motor specifications. This is for reference only and cannot be changed except by new specifications. |
|
Motors can be modeled for the power flow solution in several different ways.
|
|
|
Provides an easy way of adjusting the total motor load used in determining power flows. By changing the scaling factor, the actual Hp (total connected value) entered in the Hp field can remain static. This reduces modeling errors and eliminates multiple databases for different contingencies. |
|
|
SCADA data is derived from real time, or metered data, and converted to an ASCII format which can be read into EasyPower. SCADA data is read in as a 100% scaling factor load. The load value is multiplied by the user-defined scaling factor. This provides a way to adjust SCADA loads to form new cases. |
|
|
kW |
The kW value as read in from the SCADA ASCII file. |
|
kVAR |
The kVAR value as read in from the SCADA ASCII file. |
|
SCADA data can be modeled in the power flow solution in several different ways. SCADA load type is set in the ASCII file, but you can change it.
|
|
|
Scaling Factor |
Provides an easy way of adjusting the total SCADA load used in determining power flows. By changing the scaling factor, the actual kW +j kVAR read in from the ASCII file remains static; however, the load used in the power flow is adjusted by this factor. |
| Motor Load | |
|
Load Speed Exponent |
When you run power flow calculations, the motor load is scaled based on the frequency of the AFD. Speed is proportional to frequency. The simplified load model used is: Output Power = (Rated Power) * (AFD frequency / System Frequency) ^ x. Where x is the Load Speed Exponent. If you have a machine in which the load (power) is independent of the speed, then set the exponent to 0. If machine load (power) is proportional to speed, then set the exponent to 1. Pump loads are closer to speed squared model, so set the exponent to 2. This is the default. Example: A 100HP motor rated at 60Hz is fed by AFD at 30Hz. If the Load Speed Exponent is 2, the power output at 30Hz would be: 100 * ( 30 / 60 ) ^ 2 = 25HP. |
DC Motor Power Flow Tab
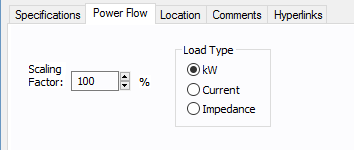
Figure 2: DC Motor Data - Power Flow
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Scaling Factor |
Ratio of actual load to connected (rated) load in percent. This is used in power flow calculations. |
|
Choose one of the following models:
|
More Information
- Motor Data
- Database Dialog Box Toolbar
- Motor - Connection Information
- Motor - Specifications Tab
- Motor - Short Circuit Tab
- Motor - TCC Tab
- Motor - Motor Starting Tab
- Motor - Harmonics Tab
- Motor - Stability Tab
- Motor - Reliability Tab
- Motor - Location Tab
- Motor - Comments Tab
- Motor - Hyperlinks Tab
- Motor - Collected Data Tab
- Motor - Media Gallery Tab
